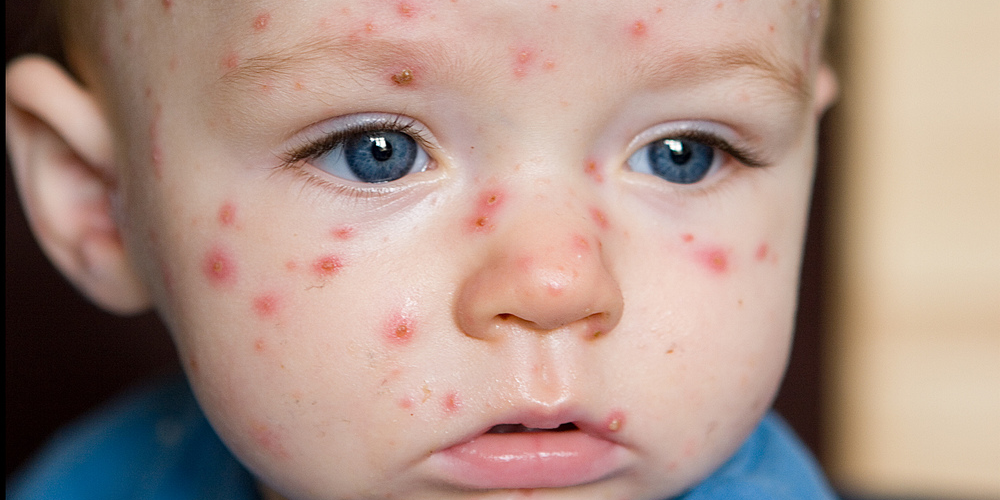
 Chickenpox is a common illness among children in the USA, especially among those who are less than 12 years of age. It's caused as a result of infection by the Varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The illness is characterized by the presence of flu-like symptoms along with the appearance of itchy rashes looking like blisters all over the child’s body.
Chickenpox is a common illness among children in the USA, especially among those who are less than 12 years of age. It's caused as a result of infection by the Varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The illness is characterized by the presence of flu-like symptoms along with the appearance of itchy rashes looking like blisters all over the child’s body.
Chickenpox or varicella vaccine can be given to children to protect from VZV infection. Moreover, even if kids who are vaccinated tend to have milder disease and recover quickly in comparison to those who are not vaccinated.
Features of Chickenpox
It Is Contagious
Chickenpox is highly contagious. Approximately 90% of the individuals who have not got the disease will get the infection after contacting with an infected person. The virus is easily spread in the air from one person to another. For instance, if you have not got the infection, you are at risk of getting it if you remain in the same room with a person suffering from chickenpox for more than 15 minutes; or if you have had face-to-face contact with a patient suffering from chickenpox such as verbal communication.
After getting infected with the virus, the time taking for the appearance of symptoms is usually 7 to 21 days (most commonly 10-14 days), this period is also referred to as incubation period.
It Can Lead to Various Complications
People who are more prone to develop complications include:
- Infants
- Adults
- Teenagers
- Pregnant females
Individuals who are immunocompromised either as a result of medication or a disease, for example, HIV/AIDS or cancer patients, patients who have organ transplants and patients who are on chemotherapy or other immunosuppressive drugs or who take steroids for a long duration.
Chickenpox can lead to various complications, which are not so common in healthy individuals. Serious complications that may occur include:
- Dehydration
- Lung infection (pneumonia)
- Problems with bleeding
- Brain infection or inflammation
- Infection of the blood (sepsis)
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Infection of the bones and joints
Patients suffering from serious complications may need hospitalization as soon as possible. Death may also occur in some cases.
Signs and Symptoms of Chickenpox
Signs of Chickenpox
The first symptoms of chickenpox include:
- High temperature between 100.4 degree F and 103 degree F
- Sickness, tiredness and sluggishness
- Lack of appetite
- Pain in head and throat
The usual course of chickenpox is around 5-10 days. The telltale sign of chickenpox infection is the development of rashes, which begin on the back and chest and later spread to the other parts of the body (scalp, face, arms and legs). The rashes may also develop on the eyelids, inside the ear, nose and vagina. The rashes itch severely and they spread for 3-4 days.
There are three phases of a rash:
- For several days, the rash appears as raised red or pink bumps, also known as papules.
- The bumps form blisters or vesicles which are filled with fluid and remains for one day.
- The blisters break and fluid is leaked, and then they become scabs and crusts. Healing takes several more days.
When to See a Doctor
No special treatment is required for majority of the cases of chickenpox. However, you should call your physician if your child has:
- High temperature lasting for greater than 4 days or is above 102 degree F
- Severe cough or difficulty in breathing
- Rash that forms pus or becomes red, swollen, warm and sore
- Severe pain in head
- Drowsiness
- Difficulty looking at bright lights
- Difficulty in walking
- Confusion
- Vomiting
- Stiffness of neck
You should also call your physician if you are concerned about symptoms of complication. You may be guided by your physician to pay attention to complications and take some medicine for relieving the itching.
Treatments of Chickenpox
Home Treatment
The rashes should not be scratched. Keep fingernails short and wear gloves onthe hands.
- Take a cool bath. Add baking soda or uncooked oatmeal to the water to relieve itching.
- Dab calamine lotion on the rashes.
- Eat a soft and bland diet if there are chickenpox sores in the mouth.
- Take antipyretics for mild fever.
Medical Treatments
|
OTC |
Prescribed Medicines |
|
Acetaminophen or ibuprofen: They can be used to relieve pain and mild fever. Follow the advice of your physician while using these medications. Aspirin to relieve fever should not be given to any patient younger than20 years old. |
Chickenpox vaccine: People who are exposed to chickenpox virus may avoid the disease by getting a vaccine within 3 days or up to 5 days. The infection will be mild in such cases. |
|
Antihistamines: Oral antihistamines such as Benadryl can be given to relieve itching. Before using any antihistamine creams or lotions, take the advice from your physician. |
Immunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins are usually prescribed for people who have chronic health problems after exposure to the virus. Pregnant females and immunocompromised persons should also get an IG shot after exposure. |
|
Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed if infection develops into the chickenpox blisters. |
Antiviral medicine: Acyclovir is used in adults and patients with weak immune systems. |
Preventions of Chickenpox
1. Chickenpox Vaccine
- Children under 7 years old: In the USA, children under 7 years old receive 2 doses of chickenpox vaccine --- the first dose is administered between 12 and 15 months of age and the second dose between 4 and 6 years old.
- Children between 7 to 12 years old: Children between 7 and 12 years old who have not received the vaccine before should get two catch-up doses, given at least with a gap of three months.
- Adults: Adults who have not had the infection or have not received the vaccine are usually administered 2 doses of the vaccine at a gap of 4 to 8 weeks.
2. Avoid Contacting People with Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a contagious disease and can be easily spread via air from person to person. Therefore, avoid contacting people with chickenpox.People who are non immune or are in high risk category should especially avoid coming in contact with people with the infection.
3. Sterilization
If someone in your house has the disease, you should take special attention to sterilize your house regularly. Disinfect chairs, tables, toys or countertops which may have been touched by the infected person. Ensure that you wash the clothes and bed sheets of the infected personregularly and thoroughly.
Is the chickenpox vaccine safe? You can get the answer from the video:
