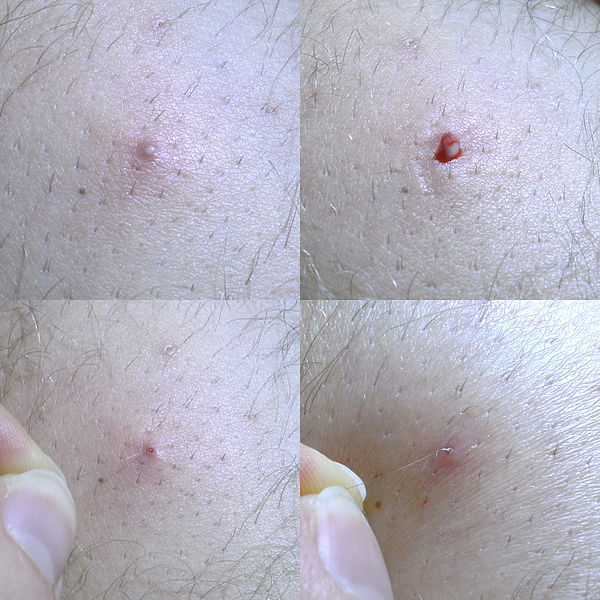
Ingrown hair is a benign condition in which a hair grows sideways into the skin. It usually appears as a small tan or pink bump on the skin. It usually occurs due to wrong shaving technique, although it can occur naturally also. Cutting the hairs very short increases the risk of hair growing sideways and piercing the skin. It can occur in clusters in a particular region if that area has been improperly shaved. It usually occurs only after puberty. They are more common in areas with coarse hairs (pubic region, face, armpit, etc.). African Americans are more likely to develop it because they have relatively thicker and coarser hairs.
What Are the Symptoms?
Pink bump on the skin accompanied by pain, itching and tenderness at the site of the bump is the most common presentation of ingrown hair. The tip of the hair may or may not be visible in the bump. Moreover, it might be cosmetically unpleasing if present on face.
Are There Any Complications?
Usually it is a benign condition that is totally innocuous. However, rarely some cosmetically unpleasing complications like scarring and skin darkening may occur.
Severe complications like skin infection (e.g. pustules) and keloid formation are relatively rare.
What Are the Treatments?
It sometimes heals on its own without any treatment. However, treatment is often needed if it fails to heal on its own. Various treatment methods available are:
- Laser Hair Removal: Laser permanently destroys the hair follicles and also prevents future growth of ingrown hair. It is more efficient and effective than electrolysis.
- Electrolysis: It permanently removes hair by destroying hair follicles. It is less efficient than laser therapy.
- Incision and Removal of Hair
- Chemical Depilatories: Nair, Veet, etc. are chemical depilatories containing calcium thioglycolate or potassium thioglycolate. They should not be used on the face. They can irritate the skin if used too often or left on skin for too long.
- Supportive Treatment to Prevent Scarring and Hyperpigmentation: (1) Fading Creams like Hydroquinone 4% etc. are used to reduce the skin discolorations caused by the problem. (2) Tretinoin Cream is used to reduce hyperkeratosis (thickening of stratum corneum layer of the skin). (3) Hydrocortisone Cream is used to reduce inflammation caused by the condition. It prevents scarring. It can also be used after the use of chemical depilatories. (4) Antibiotics (Topical Cream or Oral) may be needed if infection is suspected. Ingrown hair may get secondarily infected forming pustules or abscesses. Commonly used topical antibiotics are benzoyl peroxide, erythromycin, and clindamycin.
Usually a combination of the above listed treatments is necessary to obtain the best results.
How to Prevent It
Best method to prevent it is not to shave or wax. Using only trimmers and leaving a few millimeters stubble after trimming is as an alternative to shaving and waxing. However, if one must shave, then certain measures can reduce the chances of developing the condition. These measures are:
- Prior to shaving, the skin and the hair should be properly hydrated.
- Only shave in the direction of hair growth. Shaving "against the grain" increases the likelihood of developing the problem.
- If using electric razors for shaving, avoid touching the skin with the head of electric razor and shave slowly and gently.
- Daily washing the affected area using a washcloth or a toothbrush with soft bristles. This procedure can also be done before shaving to make skin and hairs softer.
- You can attempt to release the hair by using a sterile needle and gently dislodging it. Make sure to clean the area with 70% alcohol solution first.