 Uric acid is a substance that is present in the body in general, as it is produced as a byproduct when the digestive system breaks down purines. Foods such as, liver, anchovies, mackerels, beer and dried beans are among the purine rich items. Most often, uric acid dissolves in the blood and travels to the kidneys where it exits via urine. Sometimes, uric acid levels may increase if the body is unable to rid it via urine or if the body produces excess uric acid. This abnormal condition is known as hyperuricemia (high uric acid level). Normal uric acid levels range from 3.0 to 7.0 mg/dl and in those suffering from hyperuricemia, this level will be higher than 7.0 mg/dl. Such high levels will require medical attention and other treatment to bring down the uric acid levels to normal range.
Uric acid is a substance that is present in the body in general, as it is produced as a byproduct when the digestive system breaks down purines. Foods such as, liver, anchovies, mackerels, beer and dried beans are among the purine rich items. Most often, uric acid dissolves in the blood and travels to the kidneys where it exits via urine. Sometimes, uric acid levels may increase if the body is unable to rid it via urine or if the body produces excess uric acid. This abnormal condition is known as hyperuricemia (high uric acid level). Normal uric acid levels range from 3.0 to 7.0 mg/dl and in those suffering from hyperuricemia, this level will be higher than 7.0 mg/dl. Such high levels will require medical attention and other treatment to bring down the uric acid levels to normal range.
Why Concern About High Uric Acid in Blood?
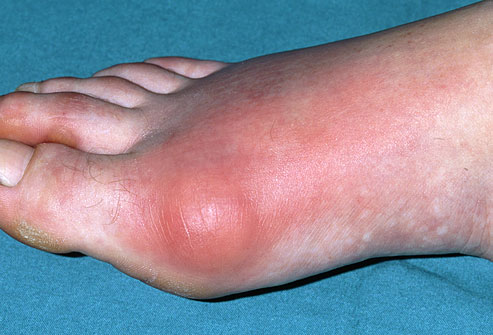
Abnormal uric acid may cause medical problems. One of the most common complications of hyperuricemia is gout. This is an inflammatory, arthritic condition that causes significant pain to the sufferer and incapacitate the affected patients. Hyperuricemia increases the risk of gout, as the uric acid build-up in the blood causes the formation of microscopic crystals in a joint. These crystals can leak into joint cartilage and cause pain when there is friction in the bones when moving. The first sign of gout is pain and inflammation of the big toe. However, gout can affect other areas of the body including ankle, heel, wrists, shoulders, pelvis and spine. Hyperuricemiacan also cause toxic waste to build up in the kidneys. Long-term hyperuricemia can therefore, cause renal failure. If such fatal conditions are developed due to excessive uric acid, the only treatment option would be dialysis or kidney transplant.
What Causes High Uric Acid in Blood?
Hyperuricemia can occur for mainly two reasons. Either it is due to the increase in uric acids caused by purine breakdown or otherwise due to an underlying medical condition. Below are some of the main causes that can lead to excessive uric acid build up in the body.
- Medications - Some medications can cause a buildup of uric acid levels and if these are being prescribed for long-term treatment, the doctors should be alerted to this drug side effect. For instance, ccertain chemotherapy drugs, diuretics or "water pills", and medications used for treating Parkinson's disease may increase uric acid levels.
- Kidney Diseases - Hyperuricemia can occur when the kidneys are unable to flush the purines out of the body because of various kidney diseases or kidney damage.
- Endocrine Conditions - Metabolic or endocrine conditions such as diabetes or acidosis can also increase uric acid levels in the blood.
- Certain Disorders - Disorders, such as, preeclampsia, obesity, cirrhosis, psoriasis and hypothyroidism can also cause hyperuricemia.
- Certain Diseases - Diseases such as Hodgkin disease, sickle cell disease and an inherited gene disorder known as Lesch-Nyhan syndrome also contribute to hyperuricemia.
- Lifestyle Factors - Exercise enhances tissue breakdown and decreases renal excretion. This too may increase uric acid levels. Starvation or crash dieting, high dietary intake of fructose and consuming foods high in purines all contribute to hyperuricemia risk.
How to Lower High Uric Acid in Blood
When diagnosed with high uric acid levels, medical treatments will be prescribed by the doctors. These treatments will be two pronged, aiming to reduce the pain through anti-inflammatory drugs and secondly to treat the underlying cause that is resulting in the uric acid buildup. Since high uric acid levels can cause gout and increase the risk of kidney stones and renal failure, it is of paramount importance to incorporate both medical and general treatment measures to manage your uric acid levels. Here are some key remedial actions to follow, in case you have elevated levels of uric acid in the blood stream.
- Avoid Foods High in Purines - Organ meats, such as, liver and anchovies and other animal meats are high in purines. Furthermore, alcohol beverages, high-fructose corn syrup, refined carbohydrates, such as white bread and cakes, also increase purine production. Cutting back on these foods can reduce uric acid levels.
- Drink Plenty of Fluids - Fluids, especially water, increases urine output, thereby, enabling the excretion of uric acid from the body. Therefore, drinking 8-16 glasses of water for a day can reduce uric acid levels.
- Lose Weight - Obesity increases the risk of various diseases. Being overweight also increases the risk of gout. Therefore, losing weight can also decrease the risk of uric acid production and the risk of gout.
- Medications - A doctor may, most often, prescribe drugs, such as uricosuric drugs, xanthine oxidase inhibitors, and NSAIDs for lowering uric acid levels. If prescribed, the results of these medications should be regularly monitored through proper checkups.
All in all, the appropriate treatment method depends on the underlying cause prompting the excessive uric acid buildup. Lowering uric acid levels is extremely necessary in avoiding its complications. Therefore, do not simply resort to anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the pain as this is only a temporary relief while long term impact of high uric acid in blood can be life threatening.
