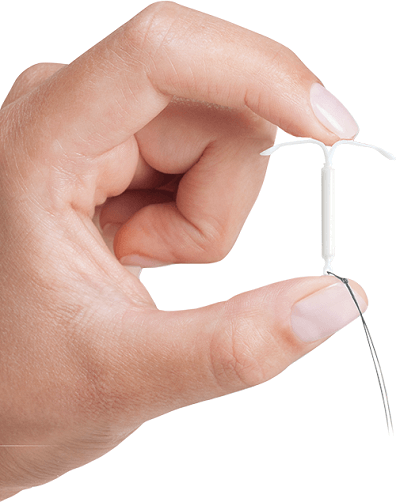
 Mirena is a hormonal intrauterine device (IUD) which is used to prevent pregnancy. The device is intended for long term use and is inserted into the uterus.
Mirena is a hormonal intrauterine device (IUD) which is used to prevent pregnancy. The device is intended for long term use and is inserted into the uterus.
How Does the Mirena Function?
Mirena is a t-shaped piece of plastic that releases progestin into the uterus. This thickens the cervical mucus which will prevent the sperm from reaching the egg and fertilizing it. This drug will also thin the lining of the uterus which can be used as a way to suppress ovulation. You can also use Mirena to help decrease the risk of developing pelvic inflammatory disease, though this will not completely eliminate the risk. Mirena will decrease menstrual pain and menstrual bleeding after three to six months in the body. You can keep Mirena in your body for up to five years after it has been inserted. Mirena can be removed at any time, which will return the user to baseline fertility.
How Is Mirena Inserted?
Before inserting a Mirena, you should bear the tips below in mind:
- Before you have Mirena inserted, you will need to visit a health care professional to perform an evaluation of your overall health.
- You will also need to submit to a full pelvic exam to ensure that your body is in the proper condition to accept Mirena. Some doctors may recommend that you undergo testing for sexually transmitted diseases before you have Mirena inserted.
- If you are breastfeeding or do not consistently use birth control, you may also need to submit to a pregnancy test before you can start using Mirena.
- You may have the device inserted any time during your menstrual cycle or while you are discontinuing the use of other birth control products. Your doctor may recommend that you take an anti-inflammatory two hours before you have the device inserted to cut down on cramping.
- Be prepared to use alternative birth control for up to one week after having the device inserted so that the drug can get into your system effectively.
Mirena releases approximately 20mg of levonorgestrel a day to help prevent pregnancy. This rate is halved after five years, making it necessary to remove the device and have a new one inserted at this time if you wish to continue using Mirena as a form of birth control. Your doctor will examine your body to determine if you can have a new Mirena device inserted immediately or if you should wait for some time after this point.
When inserting a Mirena:
- When you go to have Mirena inserted, your doctor will insert a speculum into the vagina to cleanse the cervix and vagina with antiseptic solution.
- They will then use a tool to gently align the cervical canal and uterine cavity. Then the depth of the uterine cavity will be measured. This will allow them to bend Mirena's horizontal arms to the right angle to fit it into your body.
- At this point your doctor will insert Mirena into the applicator tube and insert the tube into your uterus. Once the tube is removed, Mirena will slide into place.
- You may experience fainting, nausea, dizziness or low blood pressure while Mirena is inserted. Your doctor will tend to you accordingly if these occur.
Care Tips After Inserting a Mirena:
- You may need to visit your doctor 4 to 6 weeks after having Mirena inserted to ensure that the device has not moved or that the device is not causing pelvic inflammatory disease. If you begin showing symptoms of this disease, visit your health care provider right away as this can cause infertility if left unchecked.
- After Mirena is inserted, you should check every two months or during your period to ensure that the strings from the device are not protruding from your cervix. If they are, do not pull on the strings, but visit your doctor to have them determine whether or not the device needs to be adjusted.
Removal of the Mirena
- Mirena can be used for up to 5 years. When you would like to have the device removed, your doctor will use forceps to grab the strings and gently pull the device out of place. The arms on the Mirena device should fold upward as it is removed.
- If Mirena has become impeded in the uterine wall then you may need cervical dilation or a hysteroscopy to have the device removed. It is common to experience cramping or light bleeding during and shortly after removal.
What Are the Risks of Using Mirena?
- If you have suffered from breast, uterine or cervical cancer, have a pelvic infection or unexplained vaginal bleeding, liver disease, uterine abnormalities or sexually transmitted diseases you may not be able to use Mirena due to an increased risk of worsening your condition. Talk with your doctor about these risks before you have Mirena inserted so that you can determine what the best birth control solution is for your body.
- In some cases, it is possible to expel Mirena from the uterus. This is more likely to occur if you have heavy or prolonged periods, suffer from menstrual pain, have never been pregnant, are under the age of 20 or you had Mirena inserted immediately after childbirth or an abortion. If you have previously expelled an IUD, then you have an increased risk of doing so again. Talk with your doctor about these risks, and what to do if you expel Mirena from your body before you have the device inserted.
- There is still a chance of pregnancy while using Mirena. Less than 1 percent of users have gotten pregnant after a year of typical use with Mirena. Those who do get pregnant while using this medication are at an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, a condition where the egg implants in the fallopian tube rather than the uterus. This is very dangerous and will require medical treatment to prevent the fallopian tube from bursting. If you become pregnant while on Mirena, schedule a visit with your doctor right away to determine how to handle this situation effectively.
- Some side effects have been reported in Mirena users. These include acne, headache, breakthrough bleeding, mood changes, breast tenderness, absence of periods, ovarian cysts, weight gain and abdominal or pelvic pain. Man of these side effects get better over time and are no cause for concern. However, side effects such as the absence of periods or ovarian cysts are more likely to develop as Mirena remains in the system for a long period of time. Visit your doctor for regular checkups to determine how Mirena is affecting your body to help avoid these conditions.
- If you begin to develop signs of pregnancy, unusually heavy vaginal bleeding, pain during sex, unexplained fever, signs of heart attack or stroke, foul-smelling vaginal discharge, yellowing of the skin or eyes or if you were exposed to an STD contact your doctor right away. If this is coupled by sex being painful for your partner, Mirena's strings suddenly being longer or disappearing, you can feel part of the plastic device in your cervix or vagina or your normal periods returning then it is especially important that you get medical attention right away. These are signs that the device has moved or may be causing damage to your body.
Are There Any Interactions?
Some conditions may not be able to be treated effectively if Mirena is in your system. If you develop inflammation of the endometrium, a pelvic infection, endometrial cancer, cervical cancer, significant increase in blood pressure, or uterine or cervical perforation inform your doctor that you are using Mirena before you start your treatment. It is likely that your doctor will recommend that you have the device removed until your condition is properly treated.
You should not use barbiturates, bosentan, carbamazepine, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, rifampin, St. John's wort or topiramate while on Mirena. Talk with your doctor if you are using any of these medications to determine how to adjust your dosage to a safe level before you have the device inserted.
