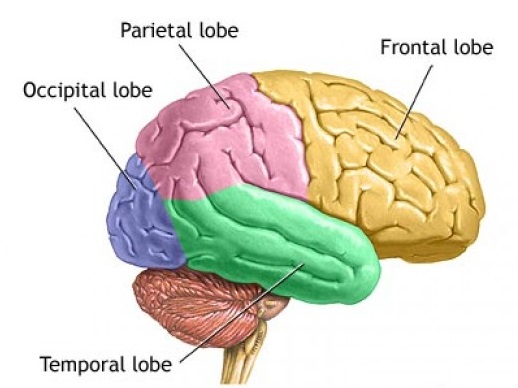
The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. Composed of 50 to 100 billion neurons, the human brain remains one of the world's greatest unsolved mysteries. Here we will take a closer look at the four lobes of the brain to discover more about the location and function of each lobe.
Brain Lobes and their Functions
The brain is divided into four sections, known as lobes (as shown in the image). The frontal lobe, occipital lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe have different locations and functions that support the responses and actions of the human body. Let's start by identifying where each lobe is positioned in the brain.
Position of the Lobes
The frontal lobe is the emotional control center of the brain responsible for forming our personality and influencing out decisions. The frontal lobe is located at the front of the central sulcus where it receives information signals from other lobes of the brain.
The parietal lobe processes sensory information for cognitive purposes and helps coordinate spatial relations so we can make sense of the world around us. The parietal lobe resides in the middle section of the brain behind the central sulcus, above the occipital lobe.
The temporal lobe is located on the bottom of the brain below the lateral fissure. This lobe is also the location of the primary auditory cortex, which is important for interpreting the sounds and the language we hear.
The occipital lobe is located at the back portion of the brain behind the parietal and temporal lobes. The occipital lobe is primarily responsible for processing auditory information.
Functions of the Lobes
The frontal lobe has many functions most of which center on regulating social behavior. Here are some of the important functions of the frontal lobe:
- Cognition, problem solving and reasoning
- Motor skill development
- Parts of speech
- Impulse control
- Spontaneity
- Regulating emotions
- Regulating sexual urges
- Planning
It is more common to injure the frontal lobe than the other lobes of the brain because the lobe is located at the front of the skull. The effects of damage to the frontal lobe often result in personality changes, difficulty controlling sexual urges, and other impulsive and risk-taking behaviors.
The parietal lobe has several functions including sensation, perception, and spatial reasoning. This lobe is responsible for processing sensory information from various parts of the body. Here are some of the functions of the parietal lobe:
- Sensing pain, pressure, and touch
- Regulating and processing the body's five senses
- Movement and visual orientation
- Speech
- Visual perception and recognition
- Cognition and information processing
Damage to the parietal lobe can result in problems with spatial reasoning, reading, writing, understanding symbols and language. Right-sided damage to the parietal area can affect a person's ability to dress or groom his or herself. While left-sided damage can result in language disorders and disorders with perception.
The temporal lobe. There are two temporal lobes located on both sides of the brain that are in close proximity to the ears. The primary function of the temporal lobes is to processing auditory sounds. Other functions of the temporal lobe include:
- Since the hippocampus, or part of the brain responsible for transferring short-term memories into long-term memories, is located in the temporal lobe, the temporal lobe helps to form long-term memories and process new information.
- The formation of visual and verbal memories.
- The interpretation of smells and sounds.
The type of impairment that results from damage to the temporal lobe depends on where the damage occurred in the lobe. Temporal lobe damage can lead to difficulty processing auditory sensations and visual perceptions, problems concentrating on visual and/or auditory stimuli, long-term memory problems, changes in personality, and changes in sexual behavior.
The occipital lobe, the smallest of the four lobes of the brain, is located near the posterior region of the cerebral cortex, near the back of the skull. The occipital lobe is the primary visual processing center of the brain. Here are some other functions of the occipital lobe:
- Visual-spatial processing
- Movement and color recognition
Since the skull protects the occipital lobe, injury is less likely to occur. However, severe damage to the occipital lobe can result in a variety of visual problems including the loss of color recognition, visual hallucinations or illusions, problems recognizing objects, and difficulty understanding language.