 The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on each side of the spine in the middle of the back, above your waist. They play important roles in cleaning your blood of waste and excess fluids, maintaining chemical balance in the blood, and helping to regulate your blood pressure.
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on each side of the spine in the middle of the back, above your waist. They play important roles in cleaning your blood of waste and excess fluids, maintaining chemical balance in the blood, and helping to regulate your blood pressure.
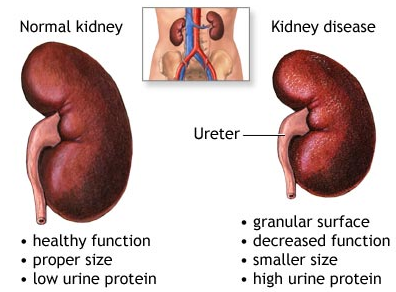
Kidney disease may result in fluid and waste product accumulation in the body, which may lead to kidney failure. This can cause symptoms like body swelling, shortness of breath, weakness and poor sleep. Kidney problems must be treated immediately to prevent loss of function, which may be a serious, life-threatening condition.
List of Kidney Problems
1. Acute Kidney Injury
Acute injury to the kidney can cause a sudden loss of function or acute renal failure. This may occur due to:
- Trauma with significant blood loss
- Sudden blood flow reduction in the kidneys
- Septic shock, which is due to severe infection
- Urinary obstruction, which may be due to an enlarged prostate
- Drug toxicity
- Complications of pregnancy
- Muscle breakdown and dehydration, which are common in athletes
2. Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic kidney disease occurs when kidney damage causes a decrease in function lasting longer than three months. Its early stage may have few or no symptoms, and it may not be noticed until significant loss of kidney function occurs. It may progressively lead to end-stage kidney failure, which will require dialysis or kidney transplantation for a patient to survive.
Chronic kidney disease may be caused by certain diseases or conditions such as:
- Diabetes (Type 1 / Type 2)
- High blood pressure
- Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the filtering units or glomeruli of the kidney)
- Interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the tubules and other structures in the kidney)
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Chronic urinary tract obstruction
- Vesicoureteral reflux, which occurs when urine goes back up into the kidneys
- Pyelonephritis, or recurrent infection of the kidneys
Certain factors may contribute to chronic kidney problems such as:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Heart disease
- High cholesterol
- Racial factors (African-American, Asian-American, or Native American)
- Family history
- Old age
Progressive kidney problems can lead to symptoms such as:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Hiccups
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Sleep problems
- Decreased urine output
- Reduced mental abilities
- Persistent itching
- Muscle twitching and cramps
- Swelling of hands, ankles, and feet
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
These signs and symptoms are nonspecific and they may also be caused by other conditions. Furthermore, these may not appear until irreversible kidney damage has occurred.
More About Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD):
3. Kidney Cancer
Cancer of the kidneys can affect the tiny tubules inside the kidneys. Your risk of developing this disease increases as you age. Other risk factors involved are genetic factors, smoking, and chronic abuse of pain medicines. Early stages of kidney cancer may have no symptoms, but during later stages, these may manifest as a lump in the abdomen, blood in the urine, unexplained weight loss, chronic pain in the side, loss of appetite. Treatments include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, biologic therapy and targeted therapy.
4. Kidney Cysts
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs. Kidney cysts are of two types:
- Polycystic kidney disease tends to run in families. Cysts take over normal tissues and cause the kidneys to enlarge and work poorly. This eventually leads to kidney failure. Cysts may also form in the liver and other parts of the body. Symptoms include pain in the sides and back, headache, bloody urine, and urinary tract infections. Diagnosis is made by getting a family history and taking imaging tests. Treatments include special medications, dialysis, or kidney transplant.
- Acquired cystic kidney disease is common in patients who are on dialysis. Unlike polycystic kidney disease, your kidneys are of normal size and cysts are not found in other parts of the body. Cysts develop after chronic kidney disease sets in. It is often harmless and needs no treatment.
5. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are solid pieces of material that form in the kidney. They may be small or large, but most of them pass out of the body naturally. However, sometimes they may get stuck and block urine flow, causing great pain. Immediate treatment is needed if you experience symptoms such as extreme pain in the back or side, bloody urine, fever, chills, vomiting, cloudy, foul-smelling urine, and pain on urination. Tests for kidney stones may include blood tests, urine examination, and imaging tests. Treatments include endoscopic surgery, shock wave treatment, or open surgery.
6. Kidney Infection (Urinary Tract Infection)
Kidney infection is a common kidney problem. Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection include:
- Pain when urinating
- Fever and chills
- Tiredness
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pressure in the lower belly
- Cloudy and foul-smelling urine
- Back pain below ribs
Women are more likely to get kidney infections. Other risk factors include diabetes, having a catheter to drain the bladder, or spinal cord injury. Consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment. Treatment usually consists of antibiotics.
Your doctor may run tests to find out if you have kidney disease. If you have kidney failure, dialysis or a kidney transplant can replace your kidneys' normal function.
How to Protect Your Kidney to Avoid Kidney Problems
- Get medical treatment for high blood pressure.
- Control blood glucose levels if you have diabetes.
- Take medications to lower cholesterol levels.
Other ways to protect your kidneys include improvement of lifestyle factors such as:
- Stop smoking.
- Eat a healthy diet with low salt intake.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Drink alcohol moderately.
- Be careful about your consumption of coffee, sugar, chocolate, and stimulants.
- Avoid taking pasteurized fruit juices, except cranberry juice (unsweetened), which may be beneficial for your kidneys.
- Strengthen your kidney function with homemade bone stocks made from grass-fed animals.
- Drink 8 to10 glasses of water daily.
- On winter months, you may slightly increase your intake of oil and sea salt.
- Include wild caught fish, sea salt, and sea vegetables in your diet.
- Get plenty of rest and sleep.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- It is believed that fear is the emotion associated with the kidneys. Use meditation to calm your fears to avoid kidney problems.
