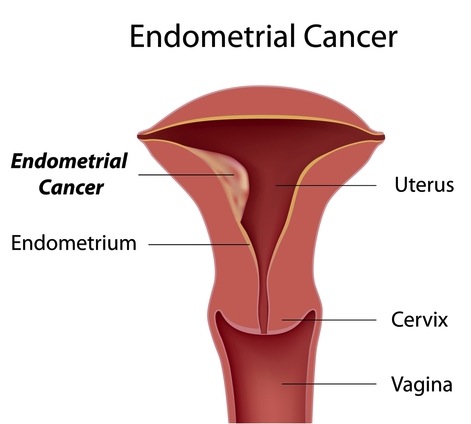
 Endometrial cancer, sometimes called uterine cancer, starts in the uterus (female pelvic organ where fetal development takes place). Endometrial cancer is more common than other types of cancer of the uterus, like uterine sarcoma and is often detected at an early stage. The main early symptom of Endometrial cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding, prompting women to see a doctor. Endometrial cancer can be cured by removing the uterus surgically.
Endometrial cancer, sometimes called uterine cancer, starts in the uterus (female pelvic organ where fetal development takes place). Endometrial cancer is more common than other types of cancer of the uterus, like uterine sarcoma and is often detected at an early stage. The main early symptom of Endometrial cancer is abnormal vaginal bleeding, prompting women to see a doctor. Endometrial cancer can be cured by removing the uterus surgically.
Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer
Some women with uterine cancer do not feel any symptoms until it has spread to other organs. However, endometrial cancer is often diagnosed by certain symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding. Most of women (9 of 10) with uterine cancer have heavy vaginal bleeding. For women in menopause this means any vaginal bleeding. Before menopause, any irregular or heavy bleeding between periods should prompt to seek immediate medical attention.
- Unexpected weight loss
- Painful urination
- Pain during sexual act
- Enlarged uterus
- Pain and weakness in the lower abdomen, legs or back
You should see your doctor as soon as possible if you have heavy and unusual vaginal bleeding or discharge.
How Is Endometrial Cancer Diagnosed?
Endometrial cancer can be diagnosed with the help of those tests and procedures:
|
Tests |
Description |
|
Sound waves or transvaginal ultrasound |
Ultrasound procedure will create a picture of your uterus, and examine the texture and thickness of the endometrium. This helps to rule out other conditions. |
|
Pelvic examination |
During this procedure, a doctor will inspect your vulva and insert two fingers of one hand into your vagina, pressing the other hand on your abdomen to feel your ovaries and uterus. Speculum, a device that opens your vagina, can also be inserted to view your cervix and vagina for any abnormalities. |
|
Hysteroscopy |
During this procedure a doctor uses a scope to inspect your endometrium. Hysteroscopy allows the doctor to examine the inside of your endometrium and uterus. |
|
Endometrial biopsy |
This procedure involves getting a sample of cells from your uterine lining for examination. Endometrial biopsy can be performed in your doctor’s office. |
|
Dilation and Curettage (D&C) |
This procedure involves surgical removal of tissue for examination under a microscope for cancerous cells. |
What Causes Endometrial Cancer?
After knowing the symptoms of endometrial cancer, let's move to its causes. Endometrial cancer is mostly diagnosed in older women over the age of 40, usually in post-menopause. The average age of patients diagnosed is 63 years. Risk factors of developing uterine cancer are:
- Never having been pregnant
- Older age
- Obesity and lack of physical activity
- Diabetes
- Early menstruation
- History of irregular periods, infertility or endometrial hyperplasia
- Fluctuations and changes in the female hormones in the body, especially an increase of hormone estrogen
- Fibroid tumors on the uterine wall
- Late menopause
- Medications used to treat breast cancer, such as Tamoxifen
- Ovarian tumors
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer, or colon cancer syndrome
What Causes Endometrial Cancer And What Are The Symptoms of Endometrial Cancer from Mayo Clinic Expert:
Can Endometrial Cancer Be Prevented?
In most cases endometrial cancer cannot be prevented. If you are at high risk of developing this health condition, be sure to make regular health checks. Some lifestyle changes and healthy habits can help to reduce the risk:
- Exercise regularly and watch your wright
- See your doctor if you are considering hormone post-menopause therapy, to evaluate risks related to uterine cancer
- Use oral contraceptives for at least one year
How Is Endometrial Cancer Treated?
Knowing the causes and symptoms of endometrial cancer is not enough, you should also how treat it to help those suffering from this condition:
Surgical Removal
The most effective treatment of endometrial cancer is surgery. Surgical treatment helps to stop the reoccurrence of cancer as well as to prevent it in women who are at high risk of developing this condition. Surgery is effective when uterine cancer has not begun to spread to other organs. The most successful surgical procedure for early stage of endometrial cancer is total hysterectomy that involves removal of ovaries, cervix, uterus and fallopian tubes.
When the Cancer Has Spread
In case if uterine cancer has spread beyond the uterus, radiotherapy is often prescribed after the surgery to eliminate the remaining cancer cells. Your doctor may recommend you an external radiotherapy (given through the skin), internal radiotherapy (using pellets placed in the vagina), or both types. Sometimes radiotherapy is recommended to the patients with large tumors, when cancer has not begun to spread to other organs.
If the cancer has spread beyond the uterus, the hormone (mostly progesterone) therapy is advised. This therapy helps to slow the growth of cancerous cells. Your doctor may also prescribe chemotherapy and radiotherapy to reduce the number of metastases and tumor size. All of these procedures can ease the symptoms of cancer and prolong your life.
Prognosis and Support
Women that are in remission need to have health checks every few months for few years. If cancer returns, it usually happens in the first 3 years. Diagnosed at the early stage, recurrent uterine cancer can be cured with intensive radiotherapy and surgery.
Most pre-menopausal women become depressed after the removal of female organs, knowing that they are no longer fertile. Joining a support group, counselling or psychotherapy may be needed in this case.
