Adrenal gland cancers occur when abnormal cells form in or travel to the adrenal glands from other parts of the body. It is often aggressive, though when found early, adrenal cancer can be cured. However, if the cancer has spread to areas of the body beyond the adrenal gland, a cure becomes less likely. Treatment can be used to delay progression or recurrence of the cancer.
What Is Adrenal Gland?
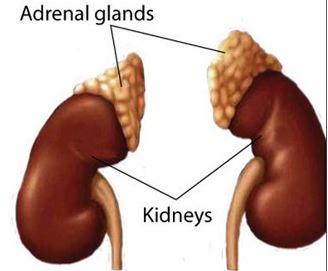
The adrenal glands are a part of the body’s endocrine system and they sit on top of the kidneys. They produce a number of essential hormones that the body needs to function normally. The glands are made up of two parts—the outer part called the cortex and the inner medulla. Adrenal cancers usually occur on the outer cortex.
When a tumor develops in the adrenal glands it can often cause too much of a particular hormone to be produced and this will depend on the part of the adrenal gland affected. Some adrenal cancers do not cause this overproduction of hormones and don't cause any obvious symptoms. These are called non-functioning tumors. A noncancerous tumor on the adrenal gland is a benign adenoma. Benign adenomas are relatively small, usually less than 2 inches in diameter. Most people with this type of tumor have no symptoms. Cancerous tumors are larger.
What Causes Adrenal Gland Cancer?
At present, the cause of adrenal gland cancer is unknown, though there are known risk factors. Those risk factors include:
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome, an inherited disorder that can cause an increase in the incidence of cancer
- Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, an abnormal growth disorder that involves the organs and body
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia, in which multiple tumors both malignant and benign occur in glands that produce hormones
- Familial adenomatous polyposis, an inherited condition that causes multiple polyp growths in the intestines
- Smoking is also believed to increase the risk of adrenal gland cancer but researchers haven’t proven it conclusively
Adrenal Gland Cancer Symptoms
Symptoms of adrenal gland cancer depend on the type of cancer you have. They include:
1. Pheochromocytoma
This is a rare tumor that is usually benign, but it can cause an overproduction of hormones, which causes persistent or episodic high blood pressure. According to Mayo Clinic, it can result in severe damage to cardiovascular system if left untreated. The symptoms include:
- Sweating
- Headaches
- Heart palpitations
- Extreme paleness
- Extreme shakiness
- Shortness of breath
- High blood pressure
2. Neuroblastoma
This is a cancer that begins in the adrenal glands, but forms in nerve tissue and often comes on in early childhood. Neuroblastoma can also develop in the chest, other parts of abdomen, in the neck and near the spine. The symptoms include:
- Bulging eyes
- Dark circles around eyes
- Lump in neck, chest, or abdomen
- Inability to move a body part
- Trouble breathing and swollen stomach in babies
- Bluish painless lumps under the skin in babies
- Bone pain
- Unexplained weight loss
- Change in bowel habits, like diarrhea
3. Adrenocortical Carcinoma
This cancer is rare and is commonly seen in children under the age of five and adults in their 30s and 40s and can cause an overproduction of hormones. It originates in adrenal cortex. Symptoms include:
- Obesity
- Stunted height growth in children
- Flushed rounded face with pudgy cheeks
- Appearance of male characteristics (or Virilization) associated with an increase of testosterone
- A fatty rounded hump high on the back and below the neck
- Weakness
- Muscle cramps
Special notes on signs of adrenal gland cancer in children:
- Enlarged penis
- Enlarged clitoris
- Big breasts in boys
- Early puberty in girls
- Excessive hair growth (facial, pubic, and underarm)
Some other possible symptoms of adrenal gland cancer include:
- Frequent urination
- Easy bruising
- Irregular periods in women
- Depression
Adrenal Gland Cancer Diagnosis
Diagnosis of adrenal gland cancer starts with your medical history, a physical exam, and any symptoms you may be having. Blood and urine samples will be taken and there may be other test ordered. These tests include:
- Biopsy
- MRI
- Adrenal angiography
- CT scan
- PET scan
Adrenal Gland Cancer Treatment
Adrenal gland cancer can be treated and in most cases cured when caught early enough. Treatment will vary depending on the type of cancer, but treatments typically used to treat adrenal gland cancer include:
- Laparoscopic adrenalectomy—small incisions are made in the abdomen to remove the tumor using a small camera.
- Transabdominal surgery—a large incision is made in the abdomen to remove the tumor so the surgeon can check for tumors in other areas.
- Posterior surgery—an incision is made in the back to remove the tumor (the kidneys lie closer to the back).
- Thoracoabdominal surgery—an incision is made in the chest and abdomen to remove a particularly large tumor.
- Cryoablation—freezing the tumor to destroy cells if it is too large to be safely removed
- Chemotherapy or radiation—this is used to treat tumors that have spread to other parts of the body.
- Medications—Mitotane and drugs like it may be prescribed for more advanced stages of adrenal cancer to prevent the adrenal glands from producing steroids.
Adrenal Gland Cancer Prognosis
Adrenal gland cancer can return at any time so follow-up appointments with your doctor are important. You may have to take prescription hormones if you were on drugs like Mitotane for hormone suppression during your treatment.
Here is more information on Adrenal Gland Cancer:
